You already know it, although very powerful, emailing is not without risks. Among the scourges faced by professionals, today we will talk about spoofing. This fraud technique, although discreet, can lead to devastating consequences for brands and their audience. What is it exactly? How does email spoofing work, what are its consequences and most importantly, how can you protect yourself from it? We’ll tell you everything in this article.
What is email spoofing?
Email spoofing involves manipulating the sending fields of an email to make it appear as if it comes from a reliable source. Cybercriminals use this technique to deceive users, often with the goal of stealing sensitive information or spreading malware.

Modified Elements
- The “From” field: This is the sender’s email address visible to the recipient. In case of spoofing, this address is forged.
- The domain name: Fraudsters use domain names similar to those of well-known brands or companies to avoid suspicion. For example, instead of “example.com”, they might use “examp1e.com”. This resemblance deceives recipients’ eyes.
- The SMTP header: This part, hidden to regular users, contains technical information that hackers modify to mask the true origin of the email.
Difference Between Spoofing and Phishing

Although associated with phishing, spoofing is an underlying technique. The main difference is that email spoofing focuses on falsifying the sender’s address to appear legitimate, while phishing adds an extra step to trick the recipient into performing a compromising action, such as providing confidential information or clicking on a fraudulent link.
Unfortunate Consequences
For Businesses
The first consequence is damage to reputation. If a brand is associated with fraudulent emails, customers may lose trust in it, even if it is not directly responsible.
In addition to this loss of credibility, spoofers often seek to steal sensitive data, leading to major information leaks or internal system hacking. These incidents can have significant financial consequences and expose the company to legal action.
Finally, when malicious actions are associated with a company, real emails sent may automatically be classified as spam, negatively impacting its communication campaigns.
For Users
Email spoofing poses a direct threat to their online security, as they are encouraged to provide confidential information, such as passwords or banking details, believing they are interacting with a trustworthy entity. This can lead to monetary losses, identity theft, or malware installation on their devices.
The Most Commonly Used Brands for Spoofing
Certain brands are specifically targeted by cybercriminals for conducting attacks via email spoofing. In 2023, according to a study by Vade, Facebook emerged as the most affected brand, accounting for 23% of all phishing URLs. Microsoft came second, followed by companies like Crédit Agricole and Orange.
Another analysis conducted by Cloudflare also lists companies like PayPal and AT&T among the most frequently spoofed brands.
Finally, Amazon and DHL are also highly sought after by spoofers. These brands enjoy great user trust, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
Protecting Against Email Spoofing
1) Conduct Basic Checks
It is possible to spot signs of spoofing with a few simple steps:
- Verify email addresses – A careful examination of the “From” field may reveal a suspicious address.
- Analyze headers – SMTP headers contain valuable information about an email’s origin. Inconsistencies in these data may indicate spoofing.
- Check links – Hover your mouse over the links included in the email to verify their true destination.
2) Implement Authentication Protocols
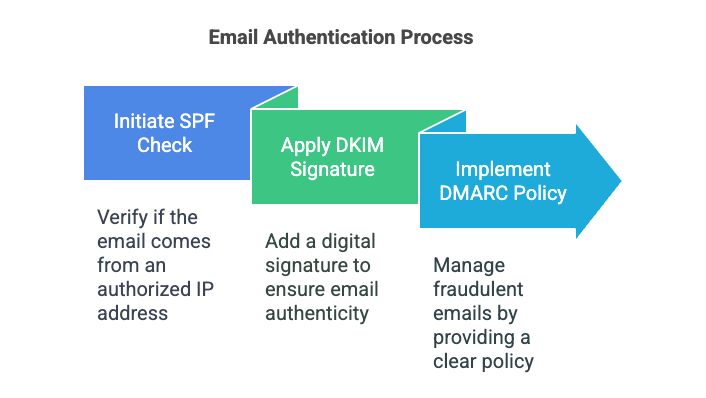
SPF (Sender Policy Framework): This protocol verifies that the email comes from an IP address authorized by the sending domain.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): It adds a digital signature to each email to ensure its authenticity.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): This standard complements SPF and DKIM to provide a clear policy on managing fraudulent emails.
3) Educate Teams and Clients
Training employees to recognize signs of a suspicious email (like an unusual address or questionable links) can prevent many attacks. For this, you can, for example, organize an annual training focused on email security. Also, encourage employees to quickly report any doubtful messages so that you can respond and counter the attack promptly.
It is also wise to keep your clients informed of spoofing risks. For instance, it is important to explain clearly that your company will never request certain sensitive information by email. Furthermore, if a phishing attempt using your organization’s identity is identified, quickly warning your clients can protect them while strengthening the trust they have in you.
With technological advances moving rapidly, cybercriminals are constantly refining their methods. Artificial intelligence could, for instance, be used to create even more convincing emails. For marketing professionals, this means constant vigilance and quick adaptation to new threats will be – and already are – essential.







