In the case of an email campaign, how do you ensure that your messages are well received, do not end up in spam, and, most importantly, do not trigger user complaints? This is where the concept of a feedback loop (FBL) comes into play. Still unfamiliar to some digital professionals, this feature is nonetheless a strategic lever to optimize deliverability and engagement. Let’s decipher this process together.
What is a feedback loop (FBL)?
The feedback loop (FBL) is a system set up by email service providers that allows email senders to receive reports on recipient complaints. Thus, when one of them reports an email as “unwanted” or “spam,” the sender is informed via a feedback loop report.
How does a feedback loop work?
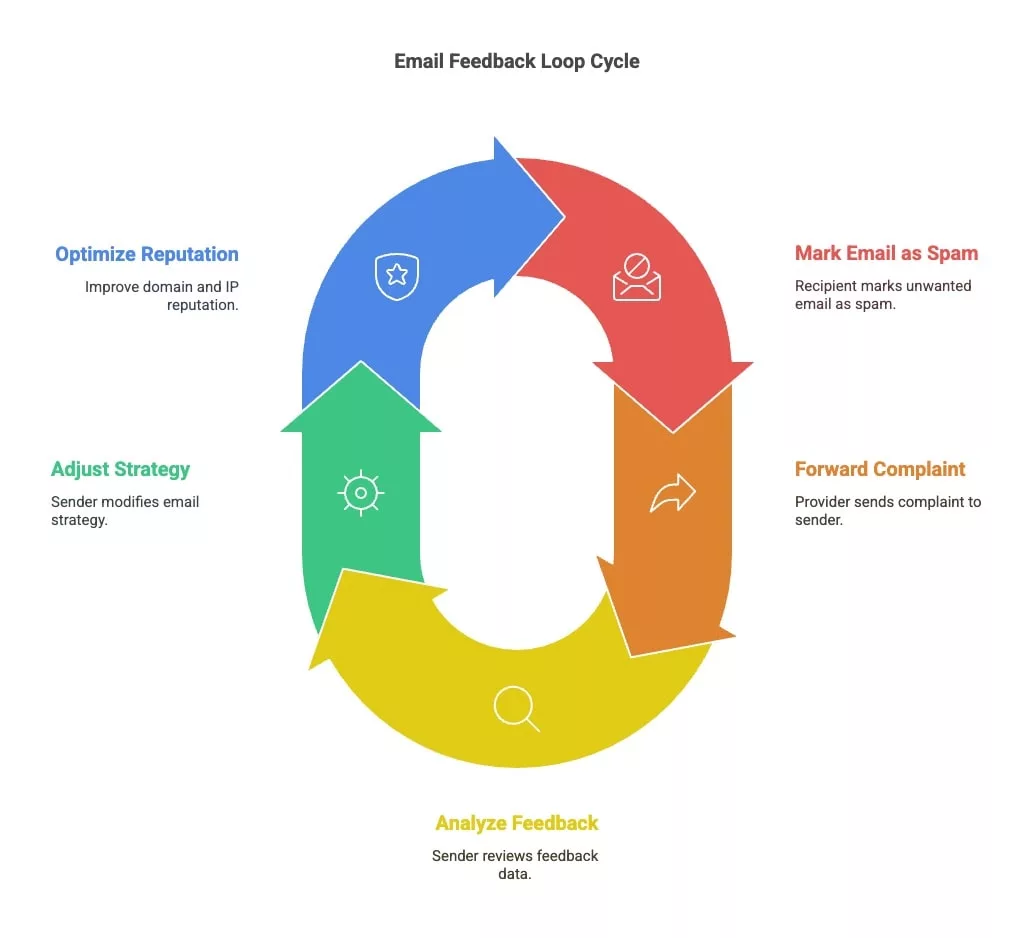
1) A recipient marks an email as spam in their mailbox.
2) The email provider forwards this complaint to the sender registered with the feedback loop program.
3) The sender can then analyze these returns, identify potential causes and adjust their sending strategy. In this way, they contribute to optimizing the reputation of their domain and IP address.
Feedback loops: benefits for everyone
Advantages for marketers
The feedback loop allows for regulating the quality of marketing sends and optimizing the deliverability of campaigns.
Better sender reputation
Email providers assign a reputation score to sending IP addresses. A high number of complaints will have a negative impact on this reputation, leading to the risk of blocking or being marked as spam. By using a feedback loop, the sender can quickly respond to complaints and reduce their frequency.
Cleaning and updating mailing lists
A golden rule in email marketing is to maintain a clean database (with CaptainVerify). A feedback loop helps identify dissatisfied subscribers and exclude them from future sends, which could otherwise worsen the situation.
Adjusting content and segmentation
If many users are complaining about a specific campaign, this indicates a problem either with the content or the segmentation. The feedback loop helps identify these friction points and adapt the strategy accordingly.
Advantages for recipients
The feedback loop also benefits email recipients by allowing them better control over their messaging experience.
Reduction of unwanted emails
When a user marks an email as “unwanted,” their feedback is considered by the sender who can thus stop sending. This reduces the number of unwanted messages in inboxes.
Better relevance of received messages
By adjusting their campaigns based on feedback loops, marketers improve the relevance of the emails sent. Recipients can then receive messages more adapted to their expectations and needs.
Improved user experience
The feedback loop allows users to better control the emails they receive by effectively filtering out unwanted messages. By forwarding complaints to senders, the FBL reduces the number of unsolicited emails, thereby ensuring a more relevant inbox and a smoother messaging experience.
How to set up a feedback loop?
Register for ISP feedback loop services
Major email providers offer FBL services accessible to legitimate senders. Among them:
- Yahoo Mail Feedback Loop
- Outlook (registration via the Junk Email Reporting Program “JMRP”)
- Gmail (does not provide a direct feedback loop, but allows complaint monitoring)
Each service has its own registration criteria, but in general, you must prove that you are an authentic sender and have a dedicated sending IP address.
Process and analyze complaint reports
Receiving FBL reports is not enough. You must use them effectively by identifying the campaigns or list segments responsible for the complaints. Then, you need to remove complainants from the database to avoid worsening the situation.
As always, feel free to try multiple approaches in your emails to reduce the number of complaints (personalizing subjects, optimizing send frequencies, etc.).
Use an FBL-compatible ESP (Email Service Provider)
Many ESPs like Mailchimp, Brevo or ActiveCampaign already integrate a feedback loop management system. Using a professional solution allows for the automation of report analysis and simplifies the management of complaint responses.
Best practices to limit complaints and optimize the Feedback Loop
Once again, we remind you of some essential points to avoid inconvenience after sending your campaigns:
- Ensure your subscribers have explicitly consented to receive your emails (double opt-in preferred).
- Use a recognizable sender and a clear subject line to avoid any confusion.
- Include a visible unsubscribe link that is easily accessible.
- Segment your lists to send relevant content to each group of subscribers.
- Test and analyze your campaigns regularly to identify dissatisfaction factors.
- Respect reasonable send frequencies to not overwhelm inboxes.
Remember: the user experience is paramount. Signing up for the feedback loop thus largely aligns with this as it helps strengthen engagement and subscriber satisfaction, maintaining your reputation and deliverability.