It is well known that a company’s reputation is crucial. But what about its online reputation, or more specifically, its reputation as an email sender? If a significant part of your communication relies on sending emails, then this factor must absolutely be taken into account. In this article, we invite you to better understand the concept of IP address reputation, implement best practices to maintain a reliable presence, and optimize the impact of your campaigns.
Understanding IP Address Reputation
The reputation of an IP address involves assessing its reliability in the context of online activities. An IP address with a good reputation is generally associated with legitimate online behavior, while a bad reputation may indicate malicious activities.
Measuring and maintaining your IP address’s reputation is crucial to ensure your emails reach their destination.

Factors Influencing IP Address Reputation
Several factors are taken into account when evaluating an IP address’s reputation. Here are the main ones to consider:
Activity History
The activity history associated with an IP address is a key indicator. IP addresses involved in suspicious or malicious activities will likely have a lower reputation.
Bounces
Bounces occur when an email server is unable to deliver an email. A high bounce rate, especially for non-existent addresses, can indicate spam activities or unverified address lists, negatively affecting the IP address’s reputation.
Spam Complaints
Spam complaints from users or recipients can significantly impact an IP address’s reputation. Email services and security providers consider the number of complaints received to assess an IP address’s reliability.
Blacklists
Blacklists managed by online security organizations compile IP addresses associated with malicious activities and reported by various sources. Presence on these lists can seriously affect an IP address’s reputation.
Traffic
Analyzing the incoming and outgoing traffic of an IP address can reveal suspicious behaviors, such as mass spamming or phishing for example, negatively impacting the reputation.
Shared IP Addresses
Often used in shared hosting environments, they can pose problems. Indeed, if other users sharing the same IP address are involved in malicious activities, this can influence the reputation of legitimate senders.
Frequency of Changes
IP addresses that change frequently can raise suspicions. This may be a sign of attempts to evade detection by constantly changing the source address of malicious activities.
The Role of Sender Score in IP Address Reputation
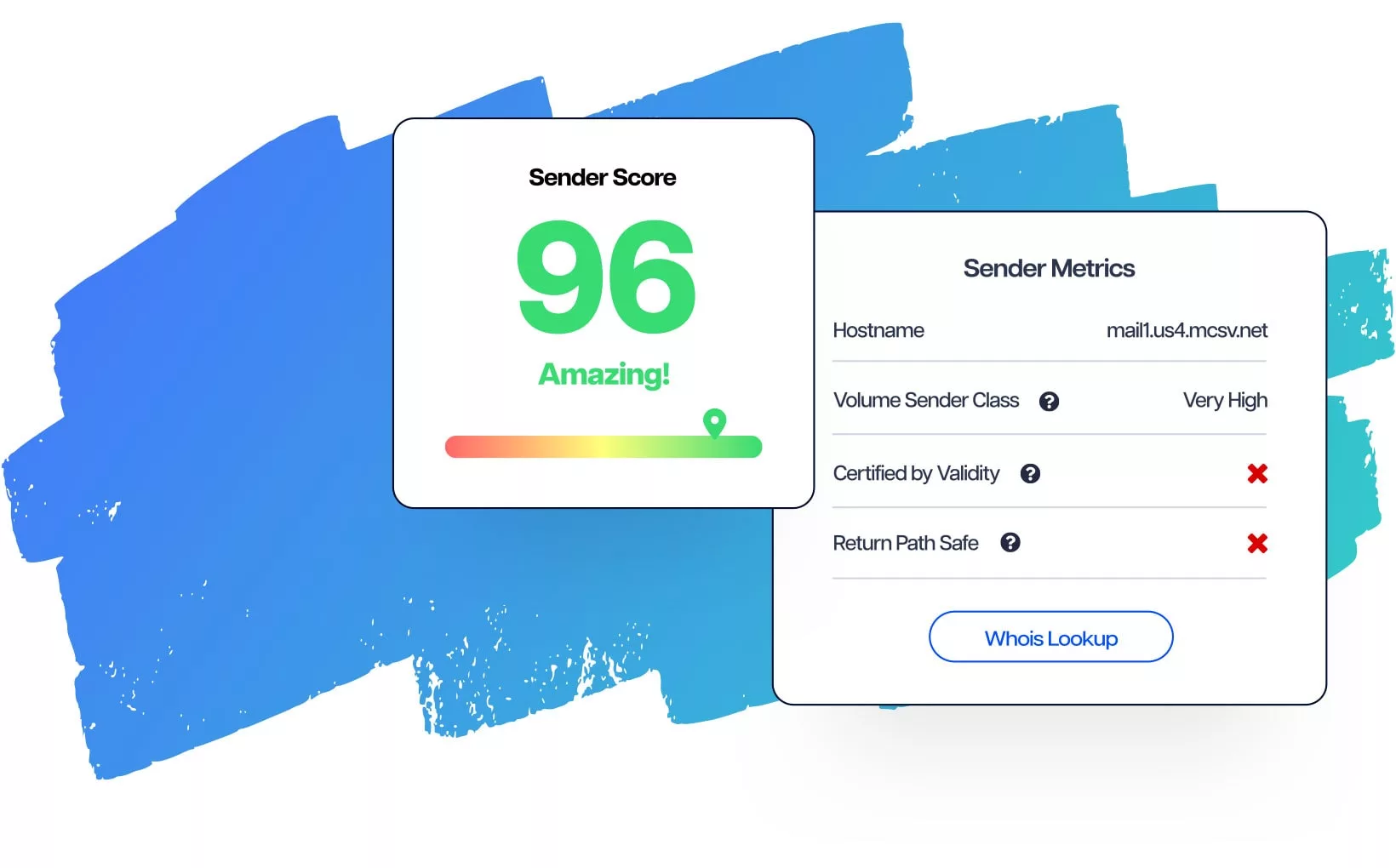
The Sender Score is a key indicator used in the email marketing field to assess an email sender’s reputation, typically associated with a specific IP address. This metric is developed and managed by Return Path, a company specialized in managing email deliverability.
The Sender Score assigns a numerical score to an IP address of a sender based on various factors related to email deliverability. The score range generally goes from 0 to 100.
A high Sender Score indicates that the sender is considered reliable, improving deliverability. Conversely, a score that is too low can lead to issues such as emails being quarantined by spam filters. The Sender Score thus allows email communication professionals to optimize their online campaigns and maintain a good reputation.
How to Boost Your IP Address Reputation
Improving your IP address’s reputation is essential to ensure the deliverability of your email sends. We therefore propose 7 effective strategies to implement:
1) Follow Good Email Sending Practices
Use DOI subscriber lists to ensure that your recipients have explicitly consented to receive your emails.
Avoid sending messages to invalid or outdated addresses, which can lead to bounces and negatively affect your reputation.
2) Manage Complaints
Regularly monitor the spam complaint rate. Reduce the number of complaints by offering users an easy way to unsubscribe and by only sending emails to interested recipients. Also, ensure that unsubscribe requests are processed promptly to prevent users from reporting your communications as spam.
3) Optimize Authentication Practices
Implement authentication protocols such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to prove that your emails are legitimate.
4) Maintain Clean Mailing Lists
Regularly clean your subscriber lists by removing outdated addresses, inactive contacts, and addresses that frequently bounce.
5) Avoid Suspicious Activities
Avoid activities that could be interpreted as spam, such as sending a large number of emails in a short period. Respect the sending limits recommended by your email provider.
6) Regularly Monitor IP Address Reputation
Use tools such as Sender Score to monitor your IP address’s reputation. Be proactive in resolving issues that could affect your score; don’t wait for them to become entrenched before addressing them.
7) Ask Users to Mark Emails as “Not Spam”
As simple as it sounds, not everyone thinks of it! Encourage recipients to mark your emails as “not spam” if they find them legitimate. This will help improve your sender reputation.
By implementing these best practices, you can gradually improve your IP address’s reputation, which will have a positive impact on the deliverability of your emails and strengthen user trust. It’s a continuous management effort to ensure a good long-term reputation.







